The lute gets its name and shape from the Arabic ‘ud. The ‘ud is an important instrument in Arabic music. It has been around for generations and is still played today. ‘Ud means the wooden one, which describes its construction. Many other instruments were made from gourds or with parchment soundboards.
What is a Lute?

This site contains affiliate links, which we receive a commission from any sale or purchase, and are of no cost to you. As a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, affiliate links will redirect you to Amazon.com and its affiliate sites. Please read our DISCLAIMER for more information
It came to Europe in the Middle Ages, perhaps brought back from the Crusades, or via Moorish Spain, or Sicily, where the thirteenth century King Manfred von Hohenstaufen was a keen player. Throughout the Mediaeval period the lute, which then had only five ‘courses’ or pairs of strings, was played with a quill plectrum—again like the ‘ud. Playing with a plectrum limits the kind of solo music that can be performed, and so the lute was often played in consort with other instruments, perhaps improvising over a drone or ground, playing dance tunes, or being used to accompany song.
Vintage Lute
History Of The Lute
The origins of the lute were in Europe during the Middle Ages. They were first played in the thirteenth century, during the time of the Crusades. Throughout the Medieval period, the lute, which was similar to the ‘Ud, was played with a plectrum. The lute was often played with other instruments. It was common to hear it improvising over other instruments, playing dance tunes, or accenting a song.

Throughout the Renaissance, the lute became one of the most popular and admired musical instruments, of the time. They were played by the greatest musicians in Europe. They became customary at the entrances of royal courts and palaces. The sound of the lute was often heard during introductions of regal events.

The lute is a very appealing instrument. It is light, portable, and easy to maintain. They are very versatile, and have been played in dance, popular, and classical music arrangements. The lute developed its own unique style, in the form of preludes, and expressive fantasias. Passemezzi, a Renaissance style of twelve-bar blues, also featured the beautiful tones of the lute.
The lute’s legacy followed the Roman cithara or lira. This was a time when people were obsessed with Classical literature. Shakespeare, among many other writers, incorporated the lute into their art. They felt the music could transport the audience into a kind of ecstasy. It was the lute’s ravishing sound which made it so admired.

The original design of a lute was similar to a modern guitar. It has six pairs of strings, tuned in fourths, and a third in the middle. The lute has a pear-shaped body, which resonates with a low gut stringing, and a delicate tone. It sounds very different from a guitar. It produces a rich, distinct sound, that feels very pure and natural.
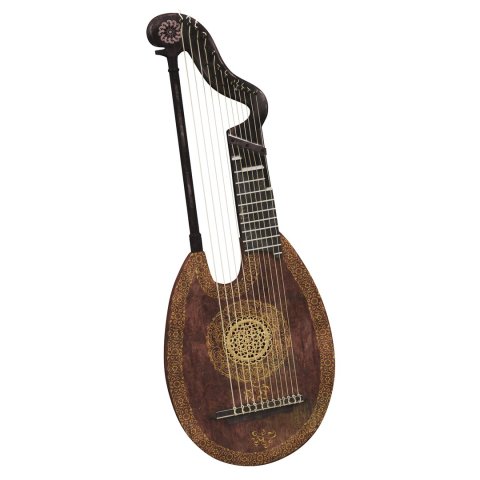

At the end of the sixteenth century experiments and innovations were made. A seventh pair of bass strings were added. They continued to add strings, up to fourteen pairs. It was to increase the instrument’s range, and allow it to play low tones, to accompany male singers.

New tuning schemes were devised. Eventually, a variety of new instruments were created, and became known as Baroque lutes. The largest of these instruments was the Roman Theorbo or Chitarrone. It was a loud bass instrument, with a long second neck, and could be up to six feet long.

The lute progressed through many eras of music, during the Golden Ages. The first was in Renaissance Italy. Francesco da Milano, like Michelangelo, was given the nickname ‘il Divino’, the divinely-inspired. He was the greatest lute player of that time, with his music, influenced by graceful, and elegant styles. Early Italian Renaissance paintings portray people dancing and lutes being played.
In Elizbethan England, the sweet-melancholy sounds of the lute were made popular by a musician named John Dowland.

In seventeenth century France the baroque lute inspired two schools of composition. Gaultiers, Dufault, de Visée and other artists created another lute-inspired style of music.
For Arabs, the lute was called the amir al – ‘alat, the sultan of instruments. In the hands of angels it symbolised the beauties of heaven; it was further used as a symbol of harmony. A lute with a broken string, as seen in Holbein’s famous painting ‘The Ambassadors,” stood for discord.

From ancient times it has symbolised youth and love. Ancient Mesopotamian relics show maidens playing long-necked lutes, in the cult of Ishtar, goddess of love and destruction. Countless images of the lute, are portrayed in love scenes, in many Renaissance paintings.
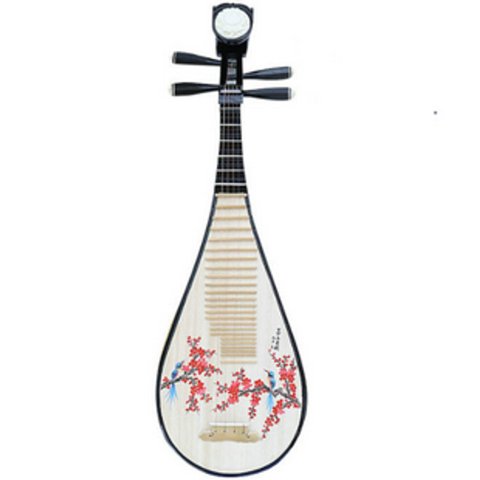

The pipa reached its height of prosperity, during the Tang Dynasty. During this time, numerous developments, like playing methodology, and repertoire expansion, became popular. This increased the pipa’s role as an accompaniment to other instruments, to becoming a prestigious instrument of its own. People began to recognize the pipa as an instrument with great soloistic capabilities.

Details Of The Lute
A lute is not a common instrument, and are not often found in local music shops. Most of the time, the small amount of lutes that are found, are of poor quality. They are usually, factory-made lutes that were designed as novelty items, instead of a serious musical instrument.

Since lutes are hard to find, it is best to find a professional luthier to purchase one. Most luthiers offer a wide selection of different instruments. If you want to purchase a lute, make sure you find a luthier, who has a lot of knowledge about the instrument.

Strings
Course means a set of two strings. A modern 12 string acoustic guitar is the same thing as a 6 course guitar or lute. Most lutes have a single top string, which is the highest pitch. This is referred to as the 1st course. Diapason refers to a bass string below the normal 6 course register.

The best lute strings were made from lamb’s gut. Most traditional lute players were particular about their strings. It was important to them to have fresh and clean sounding strings. It was a noticeable difference, between a true and a false string. They would purchase them from specific string makers at specific times of the year.

The frets, on the neck are arranged with the fret with the thickest gauge, being the closest to the nut. The first fret would be considerably thicker than the 9th fret. The next fret should be fastened with the same gauge, or with a smaller gauge. Rather than needing nine different sized frets, it is possible to fret a lute with four or five different gauges of gut string.

As long as the general fret gauge is reduced in a step wise manner until the last fret is reached. Sometimes, two or three of the same gut string can be used to tie sequential frets. The exact positioning of the frets determines the temperament and tuning of chords and intervals.
The first tempered scale was the Pythagorean scale. This is where all of the fifths, except one, are exactly in tune. The more the 5ths are in tune, the worse the 3rds sound. 3rds in the Middle Ages were considered less consonant.

Construction
Modern lutes are strung with higher tension nylon or carbon strings, instead of courses. The action and string spacing is somewhere between a traditional lute and a modern guitar. This allows guitarists the flexibility to use nails on the lute. It also allows them the ability to play both the guitar and the lute with only a small technical adjustment.
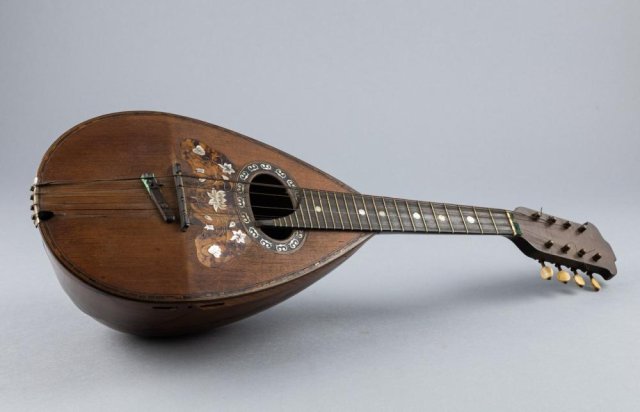

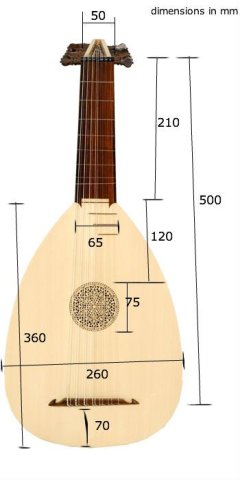
Lutes have a pear-shaped body, which is constructed from a thin, almost translucent piece of pine. This makes it lightweight and portable, but fragile. The upper layer of pine is reinforced with slightly thicker wooden bars. There is a rose hole in the center which acts as speaker for the instrument.

The delicate instrument is strung lightly to prevent it from breaking under the pressure of high tension. Early vintage versions had a fretless neck. Contemporary versions were fretted and had a finger board.
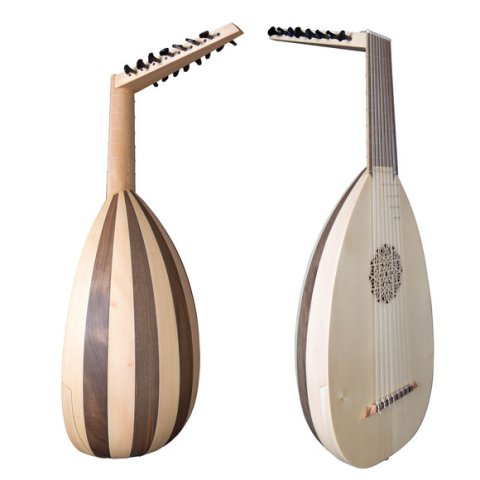


The back of a lute is made from curved, molded strips of wood. This gives the lute a bubbled look from behind. The bent strips of wood are glued together from edge to edge. The underside is made from stronger woods like sycamore, cedar, or cypress. This makes the lute stronger and more durable.to give the instrument more durability. The use of different woods, give lutes a two-toned appearance.

Lutes built at present are invariably replicas or near copies of those surviving historical instruments that are in museums or private collections. Many are custom-built, but there is a growing number of luthiers who build lutes for general sale, and there is a fairly strong, if small, second-hand market.

Because of this fairly limited market, lutes are generally more expensive than mass-produced modern instruments: factory-made guitars and violins, for example, can be purchased more cheaply than low-end lutes, but at the highest level of modern instruments, guitars and violins tend to command higher prices than lutes.


































