Bass Effects - Compressor
This site contains affiliate links, which we receive a commission from any sale or purchase, and are of no cost to you. As a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, affiliate links will redirect you to Amazon.com and its affiliate sites. Please read our DISCLAIMER for more information
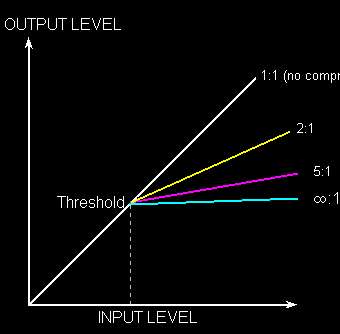
A bass compressor is easily the most often used effect used by bassists. It’s also one of the most unglamorous effects.
If you have a compressor, you will probably always use it as you play.